WebGL Definitions
Definitions learned from reading Interactive Computer Graphics: A Top Down Approach with WebGL 7th Edition
Attributes
determines the appearance of objects (color, size and width, stipple pattern, polygon mode).
Central Processing Unit
Unit which performs both the normal processing and graphical processing.
Color
colors are set in the fragment shader.
Additive Color
Forms a color by adding 3 primary colors: red, green, blue
Application color
passed to vertex shader as an uniform variable or as a vertex attribute.
Fragment color
can alter via shader code
RGB Color
8 bits per component in buffer each stored separately ranging from 0.0 to 1.0 or 0 to 255.
Subtractive Color
Forms color by filtering white light with Cyan, Magenta, and Yellow filters.
Vertex Shader Color
passed to fragment shader as varying variable.
Computer Graphics
Concerned with all aspects of producing pictures or images using a computer.
Coordinate Systems
units in points
object, world, model, problem.
clip coordinates
vertex shaders output to clip coordinates
window coordinates
pixels eventually will be produced as window coordinates. Shader must eventually produce glPosition in clip coordinates.
Depth
number of bits that are used for each pixel.
Framebuffer
Collection of pixels stored in memory.
Full-color System
24 (or more) bits per pixel.
Geometric Optics
models light sources as emitters of light energy.
GLSL
OpenGL Shading Language code sent to shaders as source code, WebGL functions compile, link and get information to shaders. No pointers.
Graphical Processing Unit
A special purpose processing unit custom-tailored to carry out specific graphics functions.
Graphics System
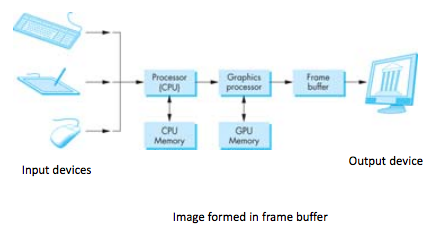
- Input Devices
- Central Processing Unit
- Memory
- Framebuffer
- Output devices
High Dynamic Range (HDR) system
A system that uses 12 or more bits per color componenet.
Image Formation
(Two-dimensional) Images are formed in an analagous process to physical imaging systems including elements of objects, viewer, and light source.
OpenGL
Cross-language/platform graphics programming library for rendering 2D and 3D vector graphics.
OpenGL ES
OpenGL for embedded systems.
Orthographic Viewing
points are projected forward along the z-axis onto the plane z=0
Photorealism
A genre of art that encompasses painting, drawing, and other graphic mediums, in which an artist studies a photograph and then attempts to reproduce the image as realistically as possible in another medium.
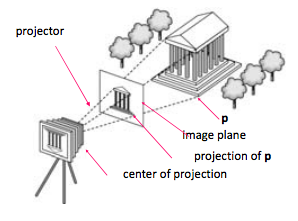
Pinhole camera
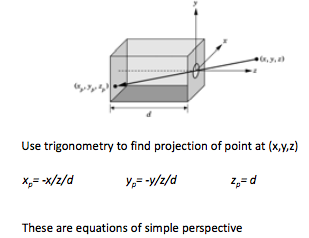 a box with a small hole in the center of one side of the box, and an ideal pinhole camera has an infinite depth of field where every point within its field of view is in focus.
a box with a small hole in the center of one side of the box, and an ideal pinhole camera has an infinite depth of field where every point within its field of view is in focus.
Pixels
Picture elements or rasters produced by the graphics system.
Precision
see Depth
Programmable Shader Pipeline
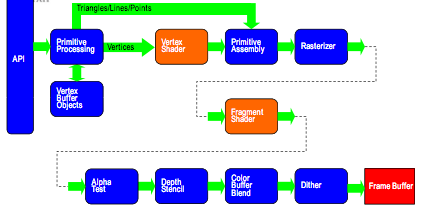
Programmer's Model
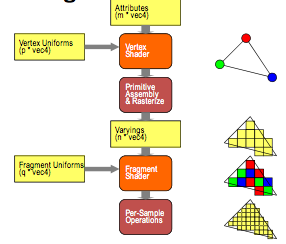
Qualifiers
Vertex attributes are interpolated by the rasterizer into fragment attributes.
Attribute Qualifier
variables that can change at most once per vertex. glPosition is a built-in one.
attribute float temperature attribute vec3 velocity
Uniform Qualifier
variables that are constant for an entire primitive. They can be changed in application and sent to shaders. Then cannot be changed in shaders. They are chiefly used to pass information to shader such as the time or bounding box of a primitive or transformation matrix.
Varying Qualifier
passed from vertex shader to fragment shader and are automatically interpolated by rasterizer
varying vec4 color;
Radiosity
An image-formation method that tries to conserve energy.
Raster
An array of picture elements displayed on an output device (see pixels).
Ray Tracing
(and photon mapping) are image-formation techniques that can form the basis for producing computer-generated images.
Resolution
The number of pixels in the framebuffer.
Shading
Smooth Shading
Default shader that uses rasterizer to interpolate vertex colors across visible polygons.
Flat Shading
Alternate shader where color in vertex determines fill color handled in shader.
Synthetic Camera Model
True-color system
See full-color system
Vertices
A set of locations in space to define or approximate objects.
Viewer
A human, camera, or digitizer that views images in space and forms images from objects.
Viewports
Do not have to use the entire window of the image. The values are pixels in window coordinates.
Visible spectrum
Visible light which has wavelengths in the range of 350 to 780 nanometers.
WebGL
An OpenGL version graphics software system supported by most modern web browsers.
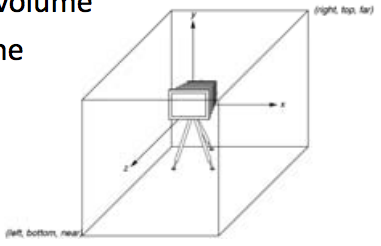
WebGL Camera
placed at the origin in object space pointing in the negative-z position. Default viewing volume is a box centered at the origin with sides of length 2.